How to scrape Google News with Python in 2023 (Full Code included)
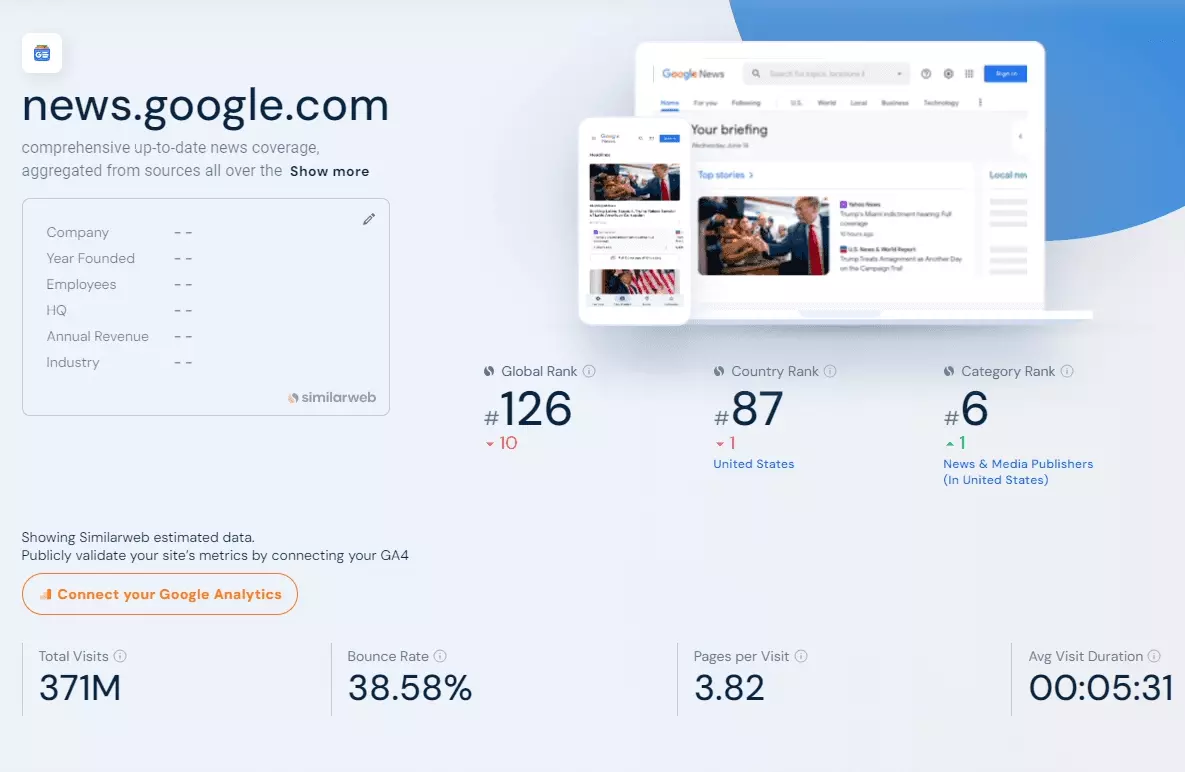
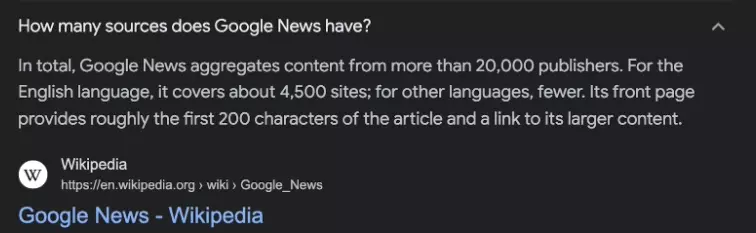
In this article, we'll explore how to scrape Google News using Python 🐍. We will walk you through the process of creating a Python script to gather news data from Google News.
Why scrape Google News?
Scraping in Python, we know how to do it. But what is our motive?
There are many reasons to scrape Google News, including:
- Brand monitoring: Track how your brand is being covered in the media.
- Competitor analysis: Monitor your competitors' activities and strategies.
- Market research: Gather data on consumer trends and market sentiment.
- News aggregation: Create your own news website or aggregator.
- Data analysis: Perform research on a variety of topics, such as politics, economics, and social issues.
Whether you're a data enthusiast, researcher, or simply someone who loves keeping up with the news, this Python script allows you to extract articles from any language or region while capturing important data like headlines, publication dates, article links, and news sources. Let's get coding! 🧑💻
How to scrape Google News with Python?
Before proceeding, we asked ourselves, what do we need exactly?
Which data attributes we want to scrape and which features we need in our scraper.
What data attributes do we need?
We want to keep it simple and straightforward. When we explore news online, we read the headline/title, when it was published, who posted it, and maybe a few words from description to understand the context.
So the attributes are sorted as follows:
- Title: headline of the news article
- Published datetime: freshness of the news
- Source: who posted the article — is it trustworthy?
- Description: what's the context
- Link: to access the complete article
What features do we need in our scraper?
Well we don’t need any fancy stuff but the scraper must be powerful enough to scrape data from several URLs and stop once a certain number of items have been collected.
Here are the features of the end scraper:
- Extract: extract all data from a given Google News Search URL
- Stop: after a limit amount of data has been collected
- Export: data to .csv with a timestamped filename
- Scale: read several Google News search URLs from a csv file
Scrape Google News with API
First we started with exploring the official API. While searching for the official API, we found out Google News had an official API till 2013 but it was deprecated in 2011 and completely discontinued in 2013.
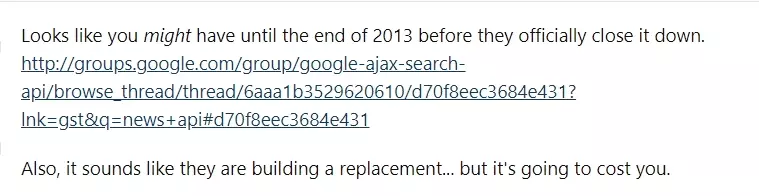
Thanks Chris.

Do we have any cost-competitive alternative — with fresh data and competitive price?
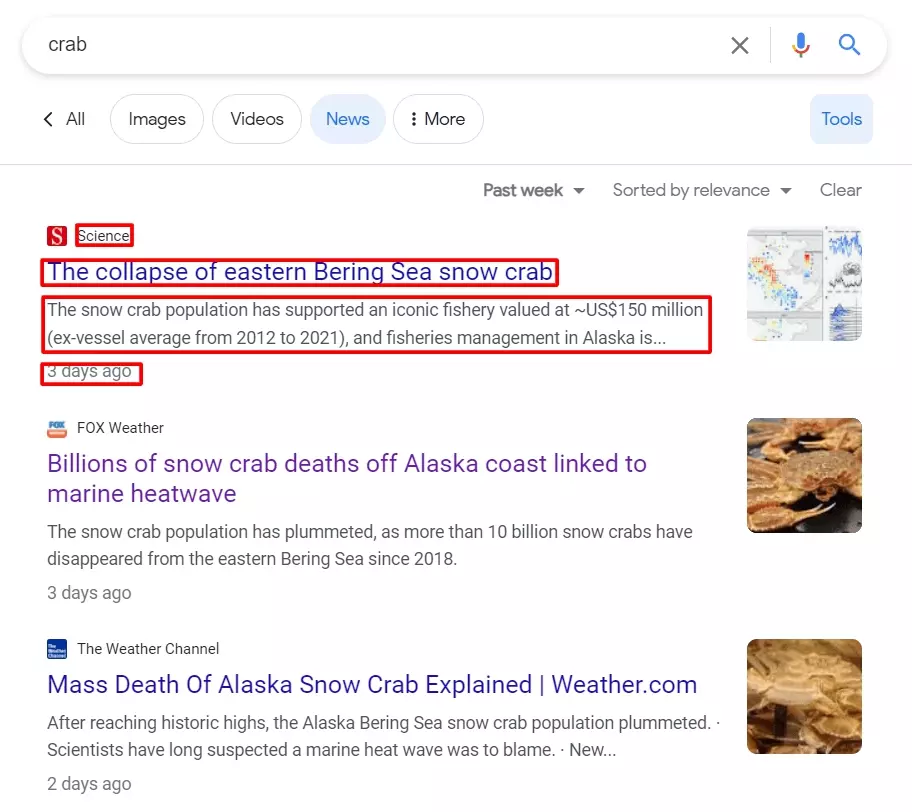
Scrape Google News through Google SERPs
Intuitively, the first idea is to pick data from Google SERPs, when using the News tab. This is, after all, the easiest way to access Google News.

But when exploring the data source, it does look that the HTML structure is extremely complex, with intricate HTML elements and meaningless class names:


If only we had another source of data, simply structured and making exhaustive data available.
Does this exist?
In the next part, we will see how to leverage the old-but-gold powerful Google News RSS feed.
Scrape Google News with RSS feed
It is actually similar to an HTML structure, apart from 3 key differences:
- Flat: the data structure is easy
- Explicit: each element has a clear explicit name
- Simple: there is no class name or additional attributes with no functional purpose
Basically, an RSS feed does look like this:
<item> <title>The Pros And Cons Of Each Cooking Method For Crab - Tasting Table</title> <link>https://news.google.com/rss/articles/CBMiRWh0dHBzOi8vd3d3LnRhc3Rpbmd0YWJsZS5jb20vMTQzOTk5My9wcm9zLWNvbnMtZWFjaC1tZXRob2QtY29vay1jcmFiL9IBAA?oc=5</link> <guid isPermaLink="false">CBMiRWh0dHBzOi8vd3d3LnRhc3Rpbmd0YWJsZS5jb20vMTQzOTk5My9wcm9zLWNvbnMtZWFjaC1tZXRob2QtY29vay1jcmFiL9IBAA</guid> <pubDate>Tue, 07 Nov 2023 12:00:40 GMT</pubDate> <description><a href="https://news.google.com/rss/articles/CBMiRWh0dHBzOi8vd" target="_blank">The Pros And Cons Of Each Cooking Method For Crab</a></description> <source url="https://www.tastingtable.com">Tasting Table</source> </item>f
And the good news is that Google News does provide an easy-to-access, highly-structured live RSS feed. Awesome!
Because of a simpler and more structured format, we will be able to develop a parser faster, and more robust in the long run.
Cherry on the cake, unlike Google SERP, the RSS feed provides a reliable exact date and time of publication for each article. To the second.

In the next part, we’ll see how to scrape Google News RSS feed.
Step-by-step tutorial
RSS provides data in a simple, structured and standardized format: it’s easier to pull and parse.

From left to right, XML feed, webpage, and HTML source code from the search Google News URL, https://news.google.com/search?q=crab&hl=en-US&gl=US&ceid=US%3Aen
To scrape data from RSS, the first thing we need is a feed URL. But where to find this Google News RSS URL?
https://news.google.com/search?q=crabhttps://news.google.com/rss/search?q=crab
Now we have the feed url, we’ll create a Google News RSS Feed scraper in 5 simple steps:
- Fetch the RSS feed using a python library
- Parse the feed and extract our required data attributes
- Add dynamic attributes for extra comfort
- Export the data to csv file
- Make it more functional
1. Fetch & Parse RSS feed
What is feedparser?
To get started, we need to install it using pip (obviously). Here’s how to do it:
$ pip install feedparserf
import feedparserf
def scrape_google_news_feed(query): rss_url = f'https://news.google.com/rss/search?q={query}&hl=en-US&gl=US&ceid=US:en' feed = feedparser.parse(rss_url)f
2. Extract data attributes
Now let’s fetch and print the entries of our Google news feed to the console. What entries to scrape? Let’s identify them on our feed page.

So we can fetch title, link, date of publication, description, and source from the RSS feed.
Let’s see how:
if feed.entries: for entry in feed.entries: title = entry.title link = entry.link description = entry.description pubdate = entry.published source = entry.source print(f"Title: {title}\nLink: {link}\nDescription: {description}\nPublished: {pubdate}\nSource: {source}") print("-+-") else: print("Nothing Found!")f
Easy!
Now let’s give our script a query and execute it.
if __name__ == "__main__": query = 'crab' scrape_google_news_feed(query)f
And here’s the output:
$ python google_news_feed_scraper.py Title: Virginia ponders reopening long-closed winter crab harvest - The Chesapeake Bay Journal Link: https://news.google.com/rss/articles/CBMilgFodHRwczovL3d3dy5iYXlqb3VybmFsLmNvbS9uZXdzL2Zpc2hlcmllcy92aXJnaW5pYS1wb25kZXJzLXJlb3BlbmluZy1sb25nLWNsb3NlZC13aW50ZXItY3JhYi1oYXJ2ZXN0L2FydGljbGVfMWZlZTYxNTItNzFhNS0xMWVlLTk3YWEtMWIzMjNiOTRlMjA3Lmh0bWzSAQA?oc=5 Description: <a href="https://news.google.com/rss/articles/CBMilgFodHRwczovL3d3dy5iYXlqb3VybmFsLmNvbS9uZXdzL2Zpc2hlcmllcy92aXJnaW5pYS1wb25kZXJzLXJlb3BlbmluZy1sb25nLWNsb3NlZC13aW50ZXItY3JhYi1oYXJ2ZXN0L2FydGljbGVfMWZlZTYxNTItNzFhNS0xMWVlLTk3YWEtMWIzMjNiOTRlMjA3Lmh0bWzSAQA?oc=5" target="_blank">Virginia ponders reopening long-closed winter crab harvest</a> <font color="#6f6f6f">The Chesapeake Bay Journal</font> Published: Mon, 23 Oct 2023 17:45:00 GMT Source: {'href': 'https://www.bayjournal.com', 'title': 'The Chesapeake Bay Journal'} -+- Title: Costa Rica Wildlife - Meet the Halloween Crab : - The Tico Times Link: https://news.google.com/rss/articles/CBMiTGh0dHBzOi8vdGljb3RpbWVzLm5ldC8yMDIzLzEwLzI0L2Nvc3RhLXJpY2Etd2lsZGxpZmUtbWVldC10aGUtaGFsbG93ZWVuLWNyYWLSAQA?oc=5 Description: <a href="https://news.google.com/rss/articles/CBMiTGh0dHBzOi8vdGljb3RpbWVzLm5ldC8yMDIzLzEwLzI0L2Nvc3RhLXJpY2Etd2lsZGxpZmUtbWVldC10aGUtaGFsbG93ZWVuLWNyYWLSAQA?oc=5" target="_blank">Costa Rica Wildlife - Meet the Halloween Crab :</a> <font color="#6f6f6f">The Tico Times</font> Published: Tue, 24 Oct 2023 21:07:00 GMT Source: {'href': 'https://ticotimes.net', 'title': 'The Tico Times'} -+-f
It works, awesome!
🎉
We’ve scraped all 5 data attributes from the RSS feed successfully.
Now let’s make this code more organized and maintainable. How do we do that? We encapsulate it in a class first.
Here’s how our updated code looks like:
import feedparser class googleNewsFeedScraper: def __init__(self, query): self.query = query def scrape_google_news_feed(self): rss_url = f'https://news.google.com/rss/search?q={self.query}&hl=en-US&gl=US&ceid=US:en' feed = feedparser.parse(rss_url) if feed.entries: for entry in feed.entries: title = entry.title link = entry.link description = entry.description pubdate = entry.published source = entry.source print(f"Title: {title}\nLink: {link}\nDescription: {description}\nPublished: {pubdate}\nSource: {source}") print("-+-") else: print("Nothing Found!") if __name__ == "__main__": query = 'crab' scraper = googleNewsFeedScraper(query) scraper.scrape_google_news_feed()f
3. Add dynamic attributes
Let’s modify the script to take a Google News URL and convert it to RSS URL.
Let’s import it first:
import argparsef
Now first, we need to define a method to convert our Google News URL to RSS url.
We can do this using:
def convert_to_rss_url(self): if "https://news.google.com/search?" in self.url: self.url = self.url.replace("https://news.google.com/search?", "https://news.google.com/rss/search?") else: raise ValueError("Invalid URL.")f
def main(): parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() parser.add_argument("-u", "--url", type=str, required=True, help="Google News URL") args = parser.parse_args() scraper = GoogleNewsFeedScraper(args.url) scraper.scrape_google_news_feed()f
Now to execute this updated code, add the final touch:
if __name__ == "__main__": main()f
Let’s execute our code now:
$ python google_news_feed_scraper.py -u "https://news.google.com/search?q=crab&hl=en-US&gl=US&ceid=US%3Aen" Title: Why 10 Billion Crabs Suddenly Vanished From the Bering Sea - Popular Mechanics Link: https://news.google.com/rss/articles/CBMiaWh0dHA6Ly93d3cucG9wdWxhcm1lY2hhbmljcy5jb20vc2NpZW5jZS9hbmltYWxzL2E0NTYxNjUxOC93aHktYmlsbGlvbnMtb2YtY3JhYnMtdmFuaXNoZWQtZnJvbS1iZXJpbmctc2VhL9IBAA?oc=5 Description: <a href="https://news.google.com/rss/articles/CBMiaWh0dHA6Ly93d3cucG9wdWxhcm1lY2hhbmljcy5jb20vc2NpZW5jZS9hbmltYWxzL2E0NTYxNjUxOC93aHktYmlsbGlvbnMtb2YtY3JhYnMtdmFuaXNoZWQtZnJvbS1iZXJpbmctc2VhL9IBAA?oc=5" target="_blank">Why 10 Billion Crabs Suddenly Vanished From the Bering Sea</a> <font color="#6f6f6f">Popular Mechanics</font> Published: Wed, 25 Oct 2023 15:45:07 GMT Source: {'href': 'http://www.popularmechanics.com', 'title': 'Popular Mechanics'} -+- Title: Virginia ponders reopening long-closed winter crab harvest - The Chesapeake Bay Journal Link: https://news.google.com/rss/articles/CBMilgFodHRwczovL3d3dy5iYXlqb3VybmFsLmNvbS9uZXdzL2Zpc2hlcmllcy92aXJnaW5pYS1wb25kZXJzLXJlb3BlbmluZy1sb25nLWNsb3NlZC13aW50ZXItY3JhYi1oYXJ2ZXN0L2FydGljbGVfMWZlZTYxNTItNzFhNS0xMWVlLTk3YWEtMWIzMjNiOTRlMjA3Lmh0bWzSAQA?oc=5 Description: <a href="https://news.google.com/rss/articles/CBMilgFodHRwczovL3d3dy5iYXlqb3VybmFsLmNvbS9uZXdzL2Zpc2hlcmllcy92aXJnaW5pYS1wb25kZXJzLXJlb3BlbmluZy1sb25nLWNsb3NlZC13aW50ZXItY3JhYi1oYXJ2ZXN0L2FydGljbGVfMWZlZTYxNTItNzFhNS0xMWVlLTk3YWEtMWIzMjNiOTRlMjA3Lmh0bWzSAQA?oc=5" target="_blank">Virginia ponders reopening long-closed winter crab harvest</a> <font color="#6f6f6f">The Chesapeake Bay Journal</font> Published: Mon, 23 Oct 2023 17:45:00 GMT Source: {'href': 'https://www.bayjournal.com', 'title': 'The Chesapeake Bay Journal'} -+-f
Our boi works smoothly.
Bravo ✨
4. Export data to csv
But we can’t keep printing the output to the console. It’ll vanish when you close your terminal or command prompt. We want to save the output sustainably.
Why not save the collected data within a .csv file?
4.1. Save data in a csv
import csvf
Now we’ll initialize an empty list to store the scraped data.
def __init__(self, url): self.url = url self.data = []f
self.data.append([self.url, title, link, pubdate, description, source])f
output_file = "google_news_output.csv" with open(output_file, "w", newline="") as csvfile: csv_writer = csv.writer(csvfile) csv_writer.writerow(["Input URL", "Title", "Link", "Published", "Description", "Source"]) for row in scraper.data: csv_writer.writerow(row)f
Now let’s check if our code saves the data to the csv file. Run the same command again:
$ python google_news_feed_scraper.py -u "https://news.google.com/search?q=crab&hl=en-US&gl=US&ceid=US%3Aen"f

And it works!
But this csv will be rewritten every time we run this script. 🤔 To avoid this, we can either prompt the user to enter a csv filename or we can generate a unique csv filename each time we run the script.
The second option is good, because it’s automated and does not required any manual commitment. Automation wins.
Let’s explore it.
4.2. Make file name unique
import timef
current_time = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S") output_file = f"google_news_{current_time}.csv"f
OK working clean!
5. Make it more functional
Let’s make our script perfect by adding additional functionality. What if we have 100 URLs to scrape? What if we need to scrape only top 10 news from each URL? Let’s solve this problem too.
We’ll thus solve both problems:
- handle multiple URLs
- add limit
Time for functionalities enhancement.
5.1. Handling multiple URLs
To make our powerful parser handle multiple URLs without a sweat, we’ll make the changes to our code.
def __init__(self): self.data = []f
converted_url = self.convert_to_rss_url(url) feed = feedparser.parse(converted_url)f
group = parser.add_mutually_exclusive_group(required=True) group.add_argument("-u", "--url", type=str, help="Google News URL") group.add_argument("-f", "--file", type=str, help="File containing Google News URLs") args = parser.parse_args()f
And to read from urls file, we added this simple condition:
if args.file: with open(args.file, "r") as url_file: urls = url_file.read().splitlines()f
Here’s how the full code looks like now:
class GoogleNewsFeedScraper: def __init__(self): self.data = [] def convert_to_rss_url(self, url): if url.startswith("https://news.google.com/search?"): return url.replace("https://news.google.com/search?", "https://news.google.com/rss/search?") else: raise ValueError("Invalid URL.") def scrape_google_news_feed(self, url): converted_url = self.convert_to_rss_url(url) feed = feedparser.parse(converted_url) if feed.entries: for entry in feed.entries: title = entry.title link = entry.link description = entry.description pubdate = entry.published source = entry.source self.data.append([url, title, link, pubdate, description, source]) else: print("Nothing Found!") def main(): parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() group = parser.add_mutually_exclusive_group(required=True) group.add_argument("-u", "--url", type=str, help="Google News URL") group.add_argument("-f", "--file", type=str, help="File containing Google News URLs") args = parser.parse_args() scraper = GoogleNewsFeedScraper() current_time = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S") output_file = f"google_news_{current_time}.csv" if args.file: with open(args.file, "r") as url_file: urls = url_file.read().splitlines() with open(output_file, "w", newline="") as csvfile: csv_writer = csv.writer(csvfile) csv_writer.writerow(["Input URL", "Title", "Link", "Published", "Description", "Source"]) for url in urls: scraper.scrape_google_news_feed(url) for row in scraper.data: csv_writer.writerow(row) else: scraper.scrape_google_news_feed(args.url) if __name__ == "__main__": main()f
5.2. Add limit
Now let’s add the limit.
def __init__(self, limit=None): self.limit = limit self.data = []f
if self.limit: entries = feed.entries[:self.limit] else: entries = feed.entriesf
parser.add_argument("-l", "--limit", type=int, help="Limit the number of results per URL") args = parser.parse_args() scraper = GoogleNewsFeedScraper(args.limit) current_time = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S") output_file = f"google_news_{current_time}.csv" if args.file: with open(args.file, "r") as url_file: urls = url_file.read().splitlines() with open(output_file, "w", newline="") as csvfile: csv_writer = csv.writer(csvfile) csv_writer.writerow(["Input URL", "Title", "Link", "Published", "Description", "Source"]) for url in urls: scraper.scrape_google_news_feed(url) for row in scraper.data: csv_writer.writerow(row) else: scraper.scrape_google_news_feed(args.url)f
Let’s test the limit and file feature.
Run the following command:
$ python google_news_feed_scraper.py -f urls.txt -l 10f
Here we go:

And with that, we’ve created a powerful multi-functionalities Google News scraper.
Here’s the full code.
import feedparser import argparse import csv import time class GoogleNewsFeedScraper: def __init__(self, limit=None): self.limit = limit self.data = [] def convert_to_rss_url(self, url): if url.startswith("https://news.google.com/search?"): return url.replace("https://news.google.com/search?", "https://news.google.com/rss/search?") else: raise ValueError("Invalid URL.") def scrape_google_news_feed(self, url): converted_url = self.convert_to_rss_url(url) feed = feedparser.parse(converted_url) if self.limit: entries = feed.entries[:self.limit] else: entries = feed.entries if feed.entries: for entry in entries: title = entry.title link = entry.link description = entry.description pubdate = entry.published source = entry.source self.data.append([url, title, link, pubdate, description, source]) else: print("Nothing Found!") def main(): parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() group = parser.add_mutually_exclusive_group(required=True) group.add_argument("-u", "--url", type=str, help="Google News URL") group.add_argument("-f", "--file", type=str, help="File containing Google News URLs") parser.add_argument("-l", "--limit", type=int, help="Limit the number of results per URL") args = parser.parse_args() scraper = GoogleNewsFeedScraper(args.limit) current_time = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S") output_file = f"google_news_{current_time}.csv" if args.file: with open(args.file, "r") as url_file: urls = url_file.read().splitlines() with open(output_file, "w", newline="") as csvfile: csv_writer = csv.writer(csvfile) csv_writer.writerow(["Input URL", "Title", "Link", "Published", "Description", "Source"]) for url in urls: scraper.scrape_google_news_feed(url) for row in scraper.data: csv_writer.writerow(row) else: scraper.scrape_google_news_feed(args.url) if __name__ == "__main__": main()f
But it looks extremely nerdy, with no documentation, nor helpful documentation. In order to ensure long-term maintainability, and ease readability, let’s tackle this now.
5.3. Garnish it with exceptions

How can we fix it?
So first we asked our AI coding partner to add exceptions to our code:

Now let’s see what it generated for us:

Now let’s add some print statements too. We’ll ask ChatGPT to add print statements to print the url we’re scraping, elapsed time, and output file to the console.

5.4. Add unforgettable chef-like signature
Last thing, like an aspiring grand chef (let’s hope so 🥹) let’s add our hot signature before running the code.
Then, let’s simply type the name of the company, and picked the font as Isometric 1:

Endly, let’s just insert it at the end of the code:
print(f"Total Elapsed Time: {total_elapsed_time} seconds") print('''~~ success ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ /\__\ /\ \ /\ \ /\ \ /\ \ /\ \ /:/ / /::\ \ /::\ \ /::\ \ \:\ \ /::\ \ /:/ / /:/\:\ \ /:/\:\ \ /:/\ \ \ \:\ \ /:/\:\ \ /:/ / /:/ \:\ \ /::\~\:\__\ _\:\~\ \ \ /::\ \ /::\~\:\ \ /:/__/ /:/__/ \:\__\ /:/\:\ \:|__| /\ \:\ \ \__\ /:/\:\__\ /:/\:\ \:\__\ \:\ \ \:\ \ /:/ / \:\~\:\/:/ / \:\ \:\ \/__/ /:/ \/__/ \/_|::\/:/ / \:\ \ \:\ /:/ / \:\ \::/ / \:\ \:\__\ /:/ / |:|::/ / \:\ \ \:\/:/ / \:\/:/ / \:\/:/ / \/__/ |:|\/__/ \:\__\ \::/ / \::/__/ \::/ / |:| | \/__/ \/__/ ~~ \/__/ \|__| ''')f
Unforgettable.
Full Code
So here’s how our complete code will look like:
import feedparser import argparse import csv import time import requests import sys class GoogleNewsFeedScraper: def __init__(self, limit=None): self.limit = limit self.data = [] def convert_to_rss_url(self, url): if url.startswith("https://news.google.com/search?"): return url.replace("https://news.google.com/search?", "https://news.google.com/rss/search?") else: return None def scrape_google_news_feed(self, url): try: converted_url = self.convert_to_rss_url(url) if converted_url is None: raise ValueError("Invalid URL.") feed = feedparser.parse(converted_url) if self.limit: entries = feed.entries[:self.limit] else: entries = feed.entries if feed.entries: for entry in entries: title = entry.title link = entry.link description = entry.description pubdate = entry.published source = entry.source self.data.append([url, title, link, pubdate, description, source]) else: print("Nothing Found!") except feedparser.FeedParserDict as e: print(f"Error parsing the feed: {e}") except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e: print(f"Network error: {e}") def main(): start_time = time.time() # Start tracking time parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() group = parser.add_mutually_exclusive_group(required=True) group.add_argument("-u", "--url", type=str, help="Google News URL") group.add_argument("-f", "--file", type=str, help="File containing Google News URLs") parser.add_argument("-l", "--limit", type=int, help="Limit the number of results per URL") args = parser.parse_args() scraper = GoogleNewsFeedScraper(args.limit) current_time = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S") output_file = f"google_news_{current_time}.csv" try: if args.file: with open(args.file, "r") as url_file: urls = url_file.read().splitlines() with open(output_file, "w", newline="") as csvfile: csv_writer = csv.writer(csvfile) csv_writer.writerow(["Input URL", "Title", "Link", "Published", "Description", "Source"]) for url in urls: print(f"Scraping URL: {url}") start_time_url = time.time() scraper.scrape_google_news_feed(url) for row in scraper.data: csv_writer.writerow(row) elapsed_time_url = time.time() - start_time_url print(f"Elapsed Time for {url}: {elapsed_time_url} seconds") print(f"Data saved to file: {output_file}") else: print(f"Scraping URL: {args.url}") start_time_url = time.time() scraper.scrape_google_news_feed(args.url) elapsed_time_url = time.time() - start_time_url with open(output_file, "w", newline="") as csvfile: csv_writer = csv.writer(csvfile) csv_writer.writerow(["Input URL", "Title", "Link", "Published", "Description", "Source"]) for row in scraper.data: csv_writer.writerow(row) print(f"Elapsed Time for {args.url}: {elapsed_time_url} seconds") print(f"Data saved to file: {output_file}") except KeyboardInterrupt: print("Operation interrupted by the user.") sys.exit(1) except ValueError as e: print(f"Invalid URL: {e}") total_elapsed_time = time.time() - start_time # Calculate total elapsed time print(f"Total Elapsed Time: {total_elapsed_time} seconds") print('''~~ success ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ /\__\ /\ \ /\ \ /\ \ /\ \ /\ \ /:/ / /::\ \ /::\ \ /::\ \ \:\ \ /::\ \ /:/ / /:/\:\ \ /:/\:\ \ /:/\ \ \ \:\ \ /:/\:\ \ /:/ / /:/ \:\ \ /::\~\:\__\ _\:\~\ \ \ /::\ \ /::\~\:\ \ /:/__/ /:/__/ \:\__\ /:/\:\ \:|__| /\ \:\ \ \__\ /:/\:\__\ /:/\:\ \:\__\ \:\ \ \:\ \ /:/ / \:\~\:\/:/ / \:\ \:\ \/__/ /:/ \/__/ \/_|::\/:/ / \:\ \ \:\ /:/ / \:\ \::/ / \:\ \:\__\ /:/ / |:|::/ / \:\ \ \:\/:/ / \:\/:/ / \:\/:/ / \/__/ |:|\/__/ \:\__\ \::/ / \::/__/ \::/ / |:| | \/__/ \/__/ ~~ \/__/ \|__| ''') if __name__ == "__main__": main()f
And here’s our output:
$ python google_news_feed_scraper.py -f urls.txt -l 5 Scraping URL: https://news.google.com/search?q=crab&hl=en-US&gl=US&ceid=US%3Aen Elapsed Time for https://news.google.com/search?q=crab&hl=en-US&gl=US&ceid=US%3Aen: 4.065908432006836 seconds Scraping URL: https://news.google.com/search?q=lobster&hl=en-US&gl=US&ceid=US%3Aen Elapsed Time for https://news.google.com/search?q=lobster&hl=en-US&gl=US&ceid=US%3Aen: 2.0368733406066895 seconds Data saved to file: google_news_2023-10-25-23-13-51.csv Total Elapsed Time: 6.106725215911865 seconds ~~ ~~ success ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ /\__\ /\ \ /\ \ /\ \ /\ \ /\ \ /:/ / /::\ \ /::\ \ /::\ \ \:\ \ /::\ \ /:/ / /:/\:\ \ /:/\:\ \ /:/\ \ \ \:\ \ /:/\:\ \ /:/ / /:/ \:\ \ /::\~\:\__\ _\:\~\ \ \ /::\ \ /::\~\:\ \ /:/__/ /:/__/ \:\__\ /:/\:\ \:|__| /\ \:\ \ \__\ /:/\:\__\ /:/\:\ \:\__\ \:\ \ \:\ \ /:/ / \:\~\:\/:/ / \:\ \:\ \/__/ /:/ \/__/ \/_|::\/:/ / \:\ \ \:\ /:/ / \:\ \::/ / \:\ \:\__\ /:/ / |:|::/ / \:\ \ \:\/:/ / \:\/:/ / \:\/:/ / \/__/ |:|\/__/ \:\__\ \::/ / \::/__/ \::/ / |:| | \/__/ \/__/ ~~ \/__/ \|__|f
And here’s the output csv file:

Complete success.
Is it legal to scrape Google News?

So all you need to take care of is not to reproduce or distribute the data that is protected by copyright. As long as you don't violate that, it's fully legal to scrape Google News.
Limitations
The RSS feed scraper has its own limitations. RSS feed only shows 100 articles per query, which means you can scrape up to maximum 100 articles.
Also the script depends on your internet connection speed. Slow internet can make them slow or abort the run.
Endly, be careful, because if pulling data too fast, your IP might be blocked. While developing our Google News Feed Parser, we scraped 15 URLs and thus did not face any ban attempt from Google.

If you want collect as many news as needed with no limitation, as well as prevent being banned at any cost, you can test our powerful no-code Google News scraper.
Conclusion
You’ll find plenty of rich programming resources. Also, try our no-code scraper to scrape Google News without a sweat.
Happy Scraping. 🦞
